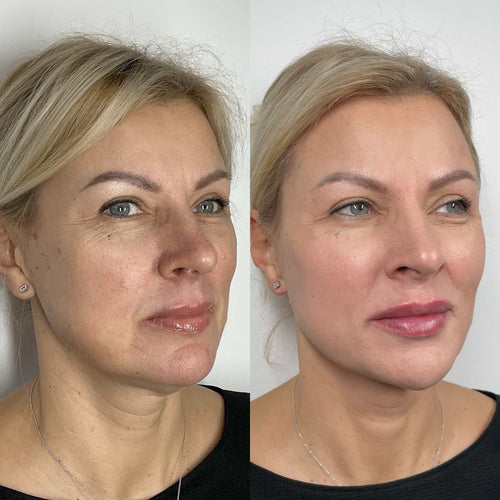
Schedule a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
# What is the Difference Between Botox and Fillers?
The distinction between Botox and fillers is a frequently asked question, especially for individuals seeking to maintain a youthful appearance without undergoing surgical procedures.
Botox, also known as botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxin used to temporarily relax facial muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines. It works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contractions.
When injected into specific areas, Botox inhibits muscle movement, effectively erasing dynamic wrinkles and creases that form over time due to repeated contractions. These wrinkles are characteristic of facial expressions, such as frowning, smiling, or raising the eyebrows.
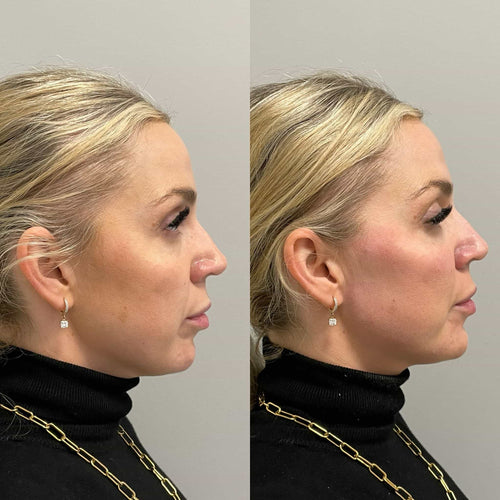
In contrast, fillers are a diverse range of injectable substances used to augment, restore, or reshape various features of the face, including lost volume, hollows, scars, or indentations. They can be made from various materials, such as hyaluronic acid (e.g., Juvederm, Restylane), calcium hydroxylapatite (e.g., Radiesse), or poly-L-lactic acid (e.g., Sculptra).
Filling agents are injected into the skin to restore lost volume, smooth out facial contours, enhance facial features, or cover scars and indentations. Unlike Botox, fillers work by adding material to the skin rather than relaxing muscles.
One of the main differences between Botox and fillers is their mechanism of action, duration of effect, and areas where they are used. Botox targets wrinkle-causing muscle contractions, while fillers address volume loss and facial asymmetries.
Another significant distinction lies in their application process. Botox injections require careful consideration and precise placement to achieve the desired effect, whereas filling agents can be applied with greater flexibility in terms of injection technique and areas treated.
Individuals seeking anti-aging treatments may choose between Botox and fillers depending on their specific concerns and goals. For instance, someone looking to reduce dynamic wrinkles might prefer Botox, while someone aiming to restore facial volume or smooth out imperfections might opt for fillers.
The key is understanding the unique characteristics of each treatment and consulting with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine which option best suits individual needs and preferences.
## h2 Effectiveness
The effectiveness of h2 in language, specifically in English, can be evaluated by examining its role in grammatical structure and its impact on clarity and readability.
h2 is used to indicate headings or subheadings in written content, serving as a way to organize and categorize information. It is commonly used in documents, articles, and websites to break up large blocks of text and provide a clear visual hierarchy of information.
In terms of effectiveness, h2 is highly effective at achieving its purpose of providing structure and organization to written content. By using h2, writers can create a clear and concise framework for their readers to follow, making it easier to understand complex information and navigate large documents.
Additionally, the use of h2 can improve the clarity and readability of text by breaking up long sentences and providing visual separation between ideas. This can lead to increased comprehension and retention of information among readers.
The effectiveness of h2 also depends on its implementation. When used correctly, h2 can enhance the overall flow and coherence of written content, while incorrect use can create confusion and disorganization.
In some cases, overuse of h2 can lead to “tag soup,” a term coined by author Bill Bryson to describe excessive use of headings that creates a cluttered and confusing visual landscape. However, when used judiciously, h2 remains an essential tool for writers and publishers looking to create clear and effective content.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of h2 has been influenced by the rise of digital publishing and the importance of accessibility in online content. With the increasing use of screen readers and other assistive technologies, properly formatted text is crucial for ensuring that all users can access and understand written content.
In conclusion, h2 is a highly effective element in language, providing structure, organization, and clarity to written content. When used correctly, it plays a vital role in creating clear and concise documents, articles, and websites that cater to diverse reader needs.
Temporary vs Permanent Results
• Botox: temporary results that can last 34 months, requiring repeated injections to maintain desired effect
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment that temporarily relaxes facial muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines.

The effects of Botox typically last for 3 to 4 months, with some patients experiencing results that can last up to 34 months, depending on individual factors such as muscle activity and injection technique.
This relatively long-lasting effect is one reason why many people choose Botox over other cosmetic treatments that provide shorter-term results.
In contrast, fillers are used to restore lost volume or smooth out wrinkles by injecting a substance into the skin, typically in the form of hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid.
The effects of fillers can vary depending on the type and brand of filler used, as well as individual factors such as skin type and desired outcome. While some fillers can last for several months to a year or more, others may need to be replenished every 6-12 months.
This means that fillers require more frequent maintenance appointments than Botox, which can be administered at intervals of 3-4 months or longer in some cases.
Another key difference between Botox and fillers is the level of reversibility. Since fillers are injected into the skin, there is a risk of complications such as lumps, nodules, or unevenness that may require removal or revision.
Botox, on the other hand, works by temporarily relaxing muscles, which means that the effects can be reversed if the injections are removed or the muscle activity increases over time.
Overall, understanding the difference between Botox and fillers is essential for making an informed decision about which cosmetic treatment is right for your individual needs and goals.
In some cases, patients may choose to combine both treatments as part of a comprehensive skincare plan. For example, Botox can be used to relax muscles that cause wrinkles, while fillers can be used to restore lost volume or smooth out deeper wrinkles.
This approach can provide longer-lasting results and a more natural-looking appearance than either treatment alone.
• Dermal fillers (e.g. hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite): permanent or semipermanent results depending on the type and placement of the filler
Dermal fillers, such as *_Hyaluronic acid_* and *_Calcium hydroxylapatite_*, are used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance facial contours.
Unlike *_Botox_*, which is a neuromodulator that temporarily relaxes muscles to reduce wrinkles, dermal fillers work by filling in the existing wrinkles with substances that mimic the body’s natural collagen and elastin.
Consult with Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers Now
The results of dermal fillers can be **semi-permanent** or **permanent**, depending on the type of filler used and where it is placed on the face. For example:
_*Hyaluronic acid fillers*, such as Restylane and Juvederm, are commonly used to treat fine lines, wrinkles, and lip augmentation. They can last anywhere from 6 months to 2 years, depending on individual factors such as age, lifestyle, and facial movement.
_*Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers*, such as Radiesse, are often used to restore lost volume in the cheeks, nasolabial folds, and marionette lines. They can last anywhere from 1-2 years.
In some cases, *_permanent_* results can be achieved with dermal fillers. For example:
_*Poly-L-lactic acid*, a type of biodegradable filler, is used to stimulate collagen production and can provide long-lasting results lasting up to 5 years or more.
Other fillers, such as *_squalane-based fillers_*, are also being developed and tested for their potential to provide longer-lasting results.
It’s worth noting that dermal fillers require regular maintenance treatments to maintain optimal results. This can include repeat injections of the same filler or switching to a different filler type to achieve desired outcomes.
In contrast, *_Botox_* is a temporary solution that requires repeated injections every 3-6 months to maintain its effects. While it may not provide the same level of longevity as dermal fillers, *_Botox_* can be a more convenient and less expensive option for certain facial concerns.
In summary, dermal fillers offer a range of benefits depending on the type of filler used, including semi-permanent or permanent results that can last from 6 months to several years. This makes them a popular choice for patients seeking long-term solutions for various facial concerns.
## h2 Mechanism of Action
When it comes to understanding the differences between Botox and fillers, one of the most critical aspects to consider is the type of result they provide.
Temporary results are achieved with the use of fillers, which are substances injected into the skin to restore lost volume or smooth out wrinkles. These results typically last anywhere from a few months to a couple of years, depending on the type of filler used and individual factors such as metabolism and lifestyle.
- Fillers can provide immediate gratification for small, temporary concerns like reducing fine lines and wrinkles around the mouth or nose.
- They are also commonly used to restore lost volume in areas like the cheeks, temples, and chin.
- The results of fillers wear off over time as the substance is broken down by the body, requiring regular touch-ups.
- Prioritize this option for individuals seeking a quick fix or temporary correction, such as those dealing with seasonal facial concerns like pumpkin patches or holiday hollowness.
In contrast, Botox provides permanent results through its unique mechanism of action.
Botox is a neurotoxin that temporarily relaxes muscles by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction.
- When injected into specific areas like frown lines or forehead creases, Botox causes long-term relaxation of those muscles, resulting in reduced wrinkle formation and appearance.
- Botox can be used to treat both facial and non-facial muscle-related issues, such as spasmodic torticollis or eyelid spasms.
- Its effects are not limited by seasonal fluctuations or natural cycles of change, providing long-term relief for many common signs of aging.
- One of the key benefits of Botox is that it addresses underlying causes rather than just symptoms, allowing users to maintain a smoother and more youthful appearance over time.
Considering these differences in results can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options, whether seeking temporary relief from small concerns or long-term solutions for deeper wrinkles and signs of aging.
How Botox and Fillers Work
• Botox: works by blocking nerve signals to muscles, temporarily relaxing facial expressions; can spread to surrounding areas (known as “eyebrow drooping”)
Botox and fillers are two popular cosmetic treatments used to achieve a more youthful appearance, but they work in distinct ways and are used to address different types of concerns.
Botox, short for Botulinum Toxin, is a neurotoxic protein that temporarily relaxes facial muscles by blocking nerve signals. When administered into a muscle, Botox prevents the muscle from contracting, resulting in a smoother appearance and reduced wrinkles and fine lines. This effect can be seen within 3-10 days of injection and typically lasts for 3-6 months.
The most common use for Botox is to treat facial expressions that are associated with aging, such as frown lines, forehead wrinkles, and crow’s feet around the eyes. By relaxing these muscles, Botox helps to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines, giving the skin a more relaxed and youthful appearance.
However, Botox can have some side effects, one of which is its ability to spread to surrounding areas. This can occur due to the way the injection is placed or if the muscle being treated is connected to other muscles through nerve branches. For example, if Botox is injected into the forehead area, it can sometimes cause “eyebrow drooping” by blocking the nerve signals that control the orbicularis oculi muscle around the eyes.
Fillers, on the other hand, are a type of cosmetic treatment used to add volume and definition to the face. They consist of a variety of substances such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid that are injected into the skin to fill in areas where there is a loss of volume due to aging.
The main purpose of fillers is to restore lost facial contours and add a more defined shape to the face. This can be achieved by filling in hollows under the eyes, augmenting the lips, or adding volume to the cheeks. Fillers are often used to address concerns such as nasolabial folds, marionette lines, and tear troughs.
Unlike Botox, fillers do not relax muscles or block nerve signals. Instead, they work by filling in empty spaces with a soft, flexible material that can be easily broken down by the body if necessary. This makes them a more versatile treatment option for a wider range of concerns and applications.
However, it’s worth noting that fillers can also have some side effects, such as swelling, bruising, or inflammation at the injection site. More serious complications, such as an allergic reaction or infection, are rare but possible.
In summary, while both Botox and fillers are popular cosmetic treatments used to address signs of aging, they work in distinct ways and are used to address different types of concerns. Botox relaxes facial muscles by blocking nerve signals, while fillers add volume and definition to the face by filling in empty spaces with a soft, flexible material.
• Dermal fillers: work by injecting a substance into the skin to replace lost volume or smooth out wrinkles and folds
Botox and dermal fillers are two popular cosmetic treatments used to address various concerns such as wrinkles, fine lines, lost volume, and skin imperfections. While both treatments can produce excellent results, they work in distinct ways.
Dermal fillers work by injecting a substance into the skin to replace lost volume or smooth out wrinkles and folds. These fillers are typically made from natural materials such as hyaluronic acid (HA), calcium hydroxylapatite, poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), or polyethylene, which are derived from plants, minerals, or synthetic compounds.
The process of using dermal fillers involves a careful analysis of the patient’s skin to determine the best placement and amount of filler required. Once the filler is injected into the desired area, it instantly provides volume and smoothness, often resulting in noticeable improvements to facial appearance.
Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Juvederm or Restylane, are highly popular due to their ease of use, flexibility, and natural integration with the skin. They can be used to address a wide range of concerns, including nasolabial folds, marionette lines, lip augmentation, and cheek contouring.
Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, such as Radiesse, are also widely used due to their ability to provide long-lasting results. They work by stimulating collagen production, which can lead to a more youthful appearance over time.
Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) fillers, such as Sculptra, are designed for longer-term use and typically require multiple injections spread out over several months or even years. These fillers stimulate collagen production and provide natural-looking results that can last up to two years or more.
When administered correctly, dermal fillers can produce dramatic improvements in facial appearance, from subtle enhancements to bold transformations. However, it’s essential for patients to choose a qualified and experienced provider who understands the intricacies of filler placement, injection technique, and potential side effects.
Aftercare instructions vary depending on the type and brand of filler used. Generally, patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, massage the treated area gently, and follow a specific schedule for follow-up appointments with their provider.
It’s essential to note that dermal fillers can cause temporary side effects such as redness, swelling, bruising, or itching at the injection site. More severe reactions are rare but may include facial asymmetry, allergic reactions, or infection. In these cases, it’s crucial for patients to follow up with their provider promptly.
Ultimately, dermal fillers offer a versatile and effective solution for addressing a wide range of cosmetic concerns, from wrinkle reduction to volume replacement. By understanding the differences between Botox and fillers, individuals can make informed decisions about which treatment best suits their unique needs and goals.
## h2 Safety and Considerations
Botox and fillers are two popular cosmetic treatments used to address a range of concerns, including wrinkles, fine lines, facial asymmetry, and volume loss. While they share some similarities, these two products work in distinct ways to produce different results.
Botox is a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It works by temporarily relaxing muscles that are responsible for causing wrinkles and fine lines on the face. When injected into a muscle, Botox blocks the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine, which normally signals the muscle to contract.
By inhibiting acetylcholine release, Botox reduces muscle activity, leading to a decrease in wrinkle formation and a smoother appearance. This effect can last anywhere from 3 to 12 months, depending on the individual and the area treated. The most common areas treated with Botox include the forehead (frown lines), between the eyebrows (glabellar lines), and around the eyes (crow’s feet).
Fillers, on the other hand, are used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, or enhance facial features. They come in a range of materials, including hyaluronic acid (HA), calcium hydroxylapatite, poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), and collagen.
Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Restylane and Juvederm, work by stimulating the body’s natural collagen production. When injected into the skin, HA filler molecules attract and retain water, swelling the treated area and filling in wrinkles and folds. The effects of HA fillers typically last between 6 to 24 months, depending on the individual and the size of the treatment area.
Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, such as Radiesse, work by replacing lost collagen fibers with a calcium-based scaffold. This scaffold stimulates the body’s natural collagen production, leading to increased tissue density and volume restoration.
Poly-L-lactic acid fillers, such as Sculptra, work differently. Instead of filling in wrinkles or restoring lost volume immediately, these fillers stimulate the body’s own collagen production over time. After an initial series of injections, Sculptra can produce lasting results that continue to improve with additional treatments.
When it comes to safety and considerations, both Botox and fillers have their own set of concerns. As with any injectable treatment, there is a risk of side effects, including bruising, swelling, redness, and pain at the injection site.
However, Botox has several unique safety considerations due to its neurotoxin properties. These include the potential for facial asymmetry, eyelid drooping, or eyebrow ptosis (drooping) if not administered correctly. Additionally, there is a rare risk of botulism, although this is extremely unlikely with proper medical supervision.
Fillers also pose certain risks, such as allergic reactions to the material, infection, and scarring. The choice of filler material can also impact safety, as some materials may be more prone to adverse reactions than others. For example, HA fillers are generally considered safe and well-tolerated, while calcium hydroxylapatite fillers have a slightly higher risk of scarring.
Before undergoing treatment with Botox or fillers, it’s essential to discuss your concerns and medical history with a qualified healthcare professional or board-certified dermatologist. They will assess your individual needs and recommend the best course of treatment to achieve your desired results while minimizing potential risks.
In addition to proper technique and patient selection, ongoing education and training are also crucial for both Botox and filler treatments. This ensures that practitioners stay up-to-date on the latest techniques, technologies, and safety considerations to provide optimal results and minimize adverse effects.
Potential Risks and Contraindications
• Botox: FDAapproved for various uses, including cosmetic and therapeutic applications; common side effects include bruising, swelling, and headaches
Botox is a widely used medication that has been approved by the FDA for various uses, including cosmetic and therapeutic applications. While it can be an effective treatment for certain medical conditions, there are also some potential risks and contraindications to consider.
One of the most common side effects of Botox is bruising, which can occur at the injection site or in areas surrounding the treated muscle. This is usually mild and resolves on its own within a few days. However, in some cases, bruising can be more severe and may require medical attention.
Another potential side effect of Botox is **swelling**, which can also occur at the injection site or in areas surrounding the treated muscle. Like bruising, swelling is usually mild and temporary, but it can be more severe in some cases.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige
In addition to bruising and swelling, Botox can also cause headaches, facial pain, and eyelid drooping in some individuals. These side effects are usually mild and short-lived, but they can be uncomfortable and may require medical attention.
There are also certain medical conditions that may make Botox contraindicated for certain individuals. For example, people with **myasthenia gravis**, a neuromuscular disorder, should not receive Botox treatment as it can worsen the condition. Additionally, people with **amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)** or other neurodegenerative disorders may also be contraindicated for Botox treatment.
Another contraindication for Botox is **pregnancy** and **breastfeeding**, as there is limited research on the safety of Botox in these situations. Additionally, people with a history of **allergic reactions** to Botox or other botulinum toxin products may also be contraindicated.
Individuals with certain eye conditions, such as **blepharospasm**, **ptosis**, or **eyelid twitching**, should use caution when receiving Botox treatment for cosmetic purposes, as the medication can exacerbate these conditions in some cases.
Furthermore, people with a history of **surgery** or **infection** at the injection site may be more susceptible to complications from Botox treatment. This is because the injection site can become inflamed or infected, which can lead to further complications.
Finally, individuals with certain neurological conditions, such as **multiple sclerosis**, **Parkinson’s disease**, or **Dystonia**, should use caution when receiving Botox treatment for therapeutic purposes, as it can exacerbate these conditions in some cases.
In terms of contraindications, Botox is generally not recommended for individuals with a history of **neuromuscular disorders**, such as myasthenia gravis or ALS. It is also not recommended for people under 18 years old, and individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding should use caution when receiving Botox treatment.
• Dermal fillers: FDAapproved for various uses, including facial rejuvenation; potential risks include skin irritation, allergic reactions, and blood clots
Dermal fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance facial features. While generally considered safe, dermal fillers do carry potential risks and contraindications that patients should be aware of.
Common Potential Risks:
-
Skin irritation: Redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site can occur in some individuals.
-
Allergic reactions: Rarely, patients may experience an allergic response to the filler material, which can manifest as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing.
-
Blood clots: There is a small risk of blood clots forming at the injection site, although this is extremely rare.
Less Common but Serious Potential Risks:
-
Facial asymmetry: Dermal fillers can cause uneven facial features if not administered correctly, leading to a lopsided appearance.
-
Eye problems: Fillers placed in the tear trough or nasolabial fold area can cause vision problems, such as blurred vision or double vision.
-
Nerve damage: Accidental injection into nerve endings can lead to numbness, tingling, or permanent loss of sensation.
Contraindications:
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The safety of dermal fillers during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well established, so it’s recommended that patients avoid these treatments during this time.
-
Active infections: Patients with active skin or facial infections should not receive dermal filler treatment until the infection has cleared up.
-
Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or taking immunosuppressive medications, may be more susceptible to complications from dermal fillers.
It’s essential for patients to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of dermal filler treatment before making an informed decision. Patients should also choose a qualified healthcare professional with experience in administering dermal fillers to minimize the risk of complications.
Read more about Lottie London Aesthetics here. Read more about Otherwheres Magazine here. Read more about Prince and Flower here. Read more about C4YL here.
